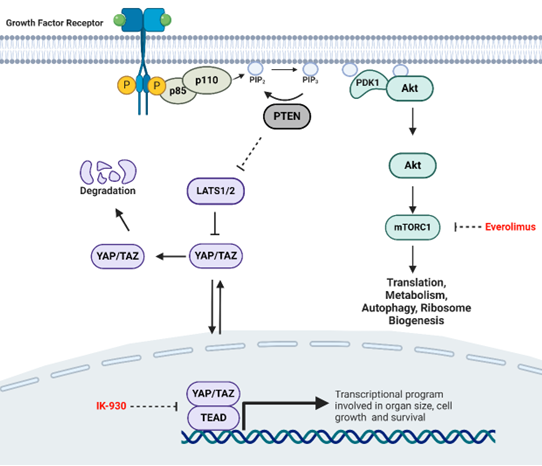
Sarcomas are cancers primarily arising from connective tissues. They represent over 50 histological types with few effective targeted therapies. Hyperactivation of PI3K, a serine/threonine kinase crucial for cell survival and proliferation is commonly observed in sarcomas due to deletion of PTEN in approximately 20-30% of sarcomas. Thus, targeting PI3K may serve as an effective potential treatment for these sarcomas. The mTORC1 complex has been well-established as a key downstream effector of PI3K signaling. We have generated additional data suggesting that YAP/TAZ represent key transcriptional effectors of PI3K signaling. mTORC1 is a regulator for protein synthesis and cell survival while YAP/TAZ, downstream targets of Hippo pathway, are transcriptional coactivators that promote sarcomagenesis and metastasis. How these two pathways coordinately mediate oncogenic PI3K signaling has been poorly studied representing a significant gap in knowledge. Tissue microarray analysis showed that approximately 46% of samples display loss of PTEN protein expression and 38% of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS) also displayed loss of PTEN expression. Various sarcoma cell lines also exhibit elevated phosphorylation of the PI3K target, Akt, as well as loss of PTEN expression. Conditional knock-out of both Wwtr1 (Taz) and Yap improves survival in a Trp53fl/fl Ptenfl/fl mouse model of UPS. RNA-Seq analysis performed on tumors from conditional mice reveals subsets of genes regulated by Wwtr1, Yap, and both Wwtr1 and Yap. Interestingly, pathway analysis showed alteration of Hippo and mTORC1 pathway in Trp53fl/fl Ptenfl/fl Wwtr1fl/fl Yapfl/fl mice tumor samples. Upon treatment with mTORC1 inhibitor, Everolimus, and YAP/TAZ inhibitor, IK-930, and we showed that monotherapy had a very modest effect on cell proliferation and growth both in vivo and in vitro. However, upon combination therapy with Everolimus and IK-930, synergistic activity was seen both in vitro and in vivo seen by significant reduction in cell growth and proliferation. The combination therapy also showed significant reduction in tumor burden in mice relative to monotherapy controls.
Our data supports the model that TAZ/YAP are key transcriptional co-activators downstream of PI3K signaling. This work suggests that TAZ/YAP as well as mTORC1 mediate oncogenic PI3K signaling. We showed that dual inhibition of mTORC1 and YAP/TAZ-TEAD can serve as an effective therapy in PI3K-activated sarcomas.